Welcome to the lesson on Python Dictionaries
Dictionaries
A dictionary is another collection of data and elements, which store values in pairs.
Unlike Lists and Tuples, dictionaries do not allow for duplicate data.
Example:
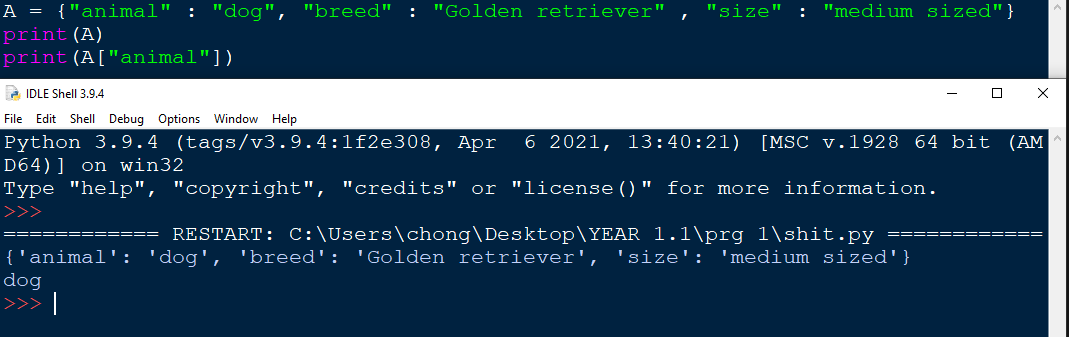
Dictionaries are created with the curly bracket in place of the round brackets. Variables or more commonly known as keys , are called and given a value / data with colon seperating them.
Accessing items stored in the dictionary
As seen from the previous example , variables can be called by using dictionary["key"]
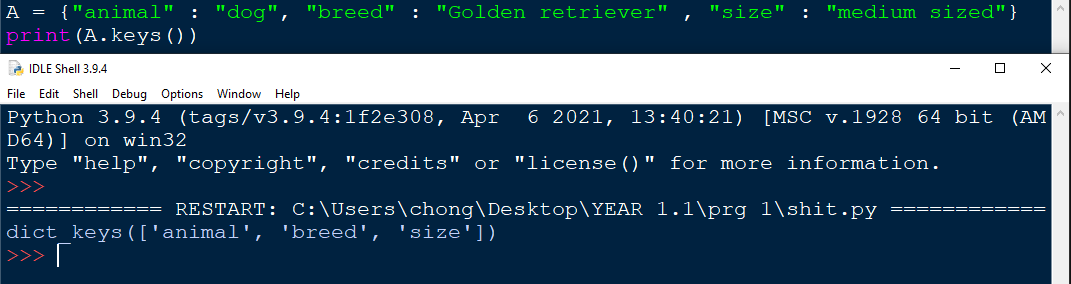
keys() function
The keys() function can be used to return all the keys within a dictionary.
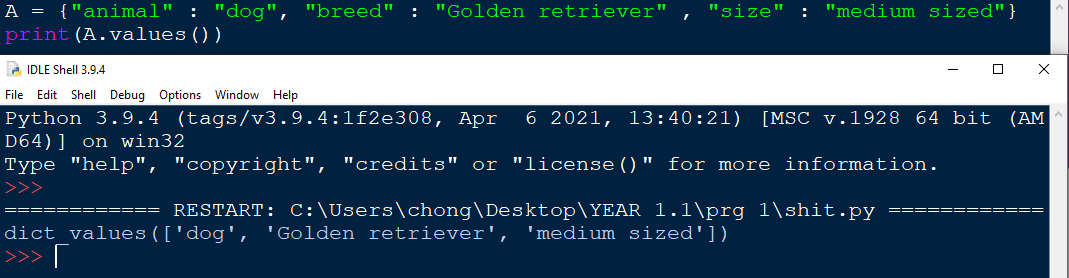
values() function
Using the values() function will return all the values stored inside the dictionary
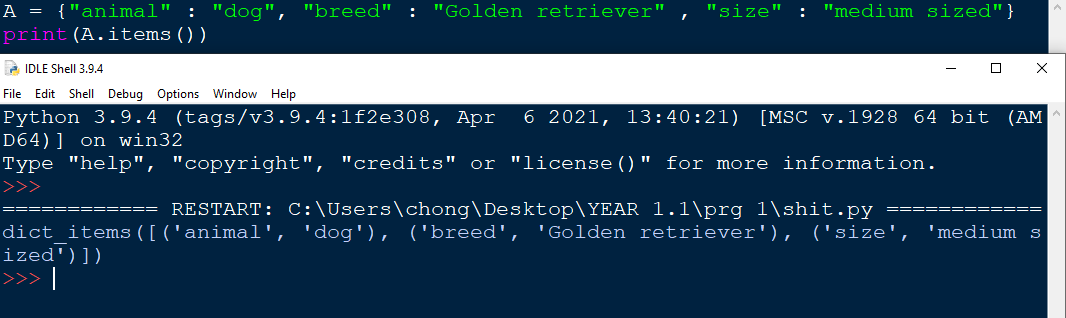
items() function
Using the items() function will return all the items stored inside the dictionary, which icnludes keys.
Updating a dictionary
Using the update() function , values in the dictionary can be changed.
Example:
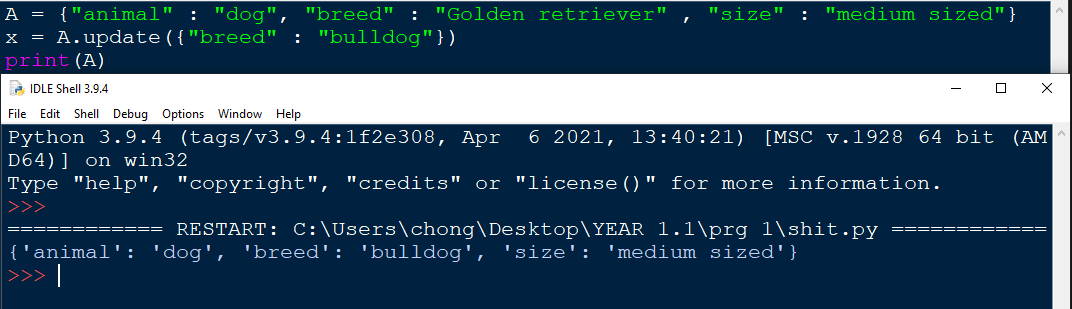
The update function is not only limited to changing the value of a key, it can also add a whole new key into the dictionary.
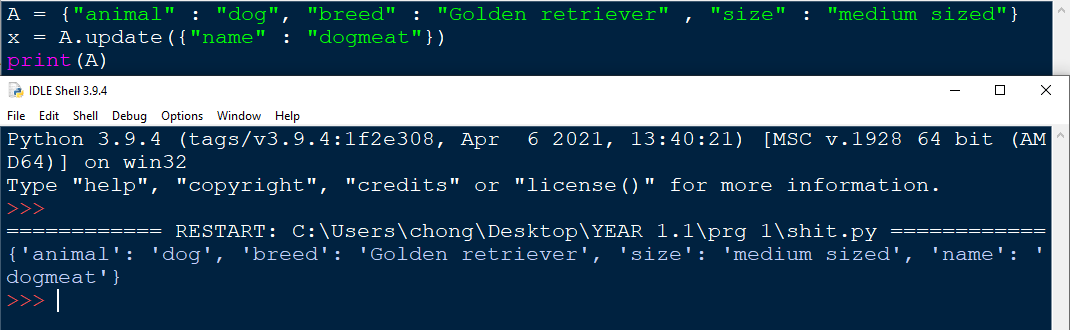
Nested dictionaries
Nested dictionaries is an advanced feature in python. It is essentially Object oriented programming. This can be used in the following example to created various objects with different attributes tied to thay object.
Example:
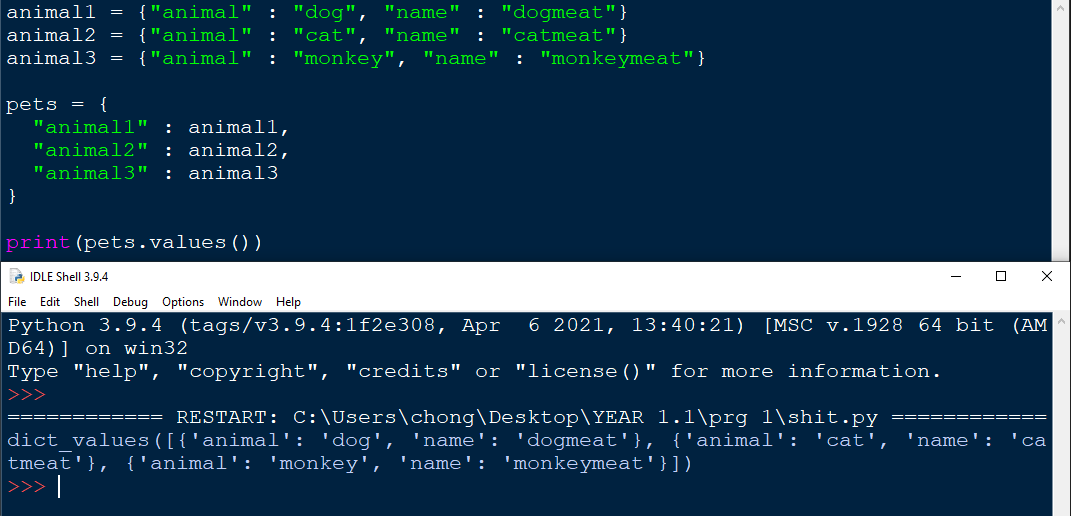
By using calling 3 dictionaries , animal1 , 2 and 3, i am able to create a fourth dictionary which acts as a class. And with that , my animal 1 2 and 3 are all linked up to a class called pets.
End of Python Dictionaries
You have learned Dictionaries in simple terms. Let's proceed on to Quiz.