Welcome to the lesson on Python Lists
Lists
A list is a collection of data , ranging from strings to numbers or a mix of both.
With the usage of lists, storing and using of data is much more efficient.
Example: creation of lists
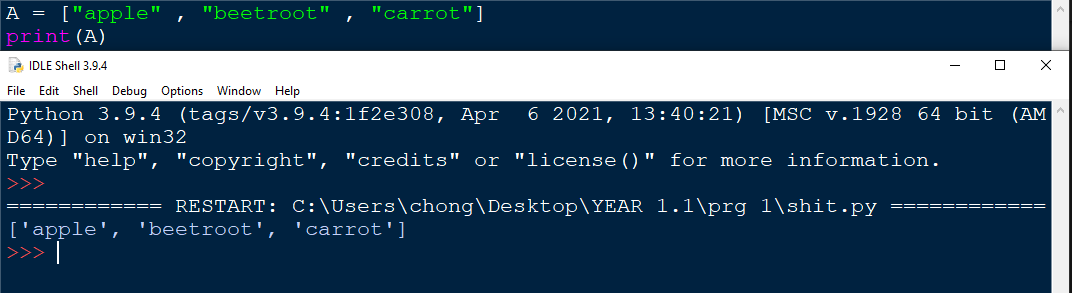
Lists are created with 2 square brackets. a comma is also put between each variable or value the user would like to store.
Lists allow for duplicate data to be stored. In addition, lists can be editted for furture use , which we will explore later on.
Indexing
The position of stored values in a list is also known as the index.
index starts from 0 and ends at the (total number of values stored - 1)
Examples:
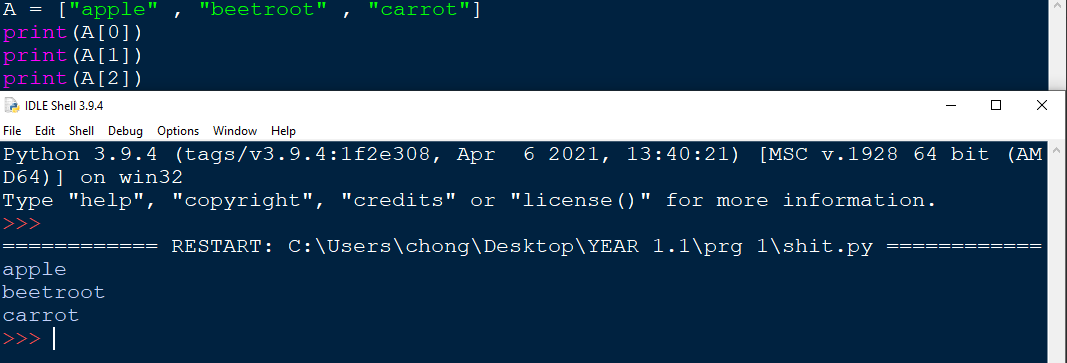
the index number is called within the squarebrackets. And infront , the name of the list.
Negative index
Negative indexing can also be used to close down on a position
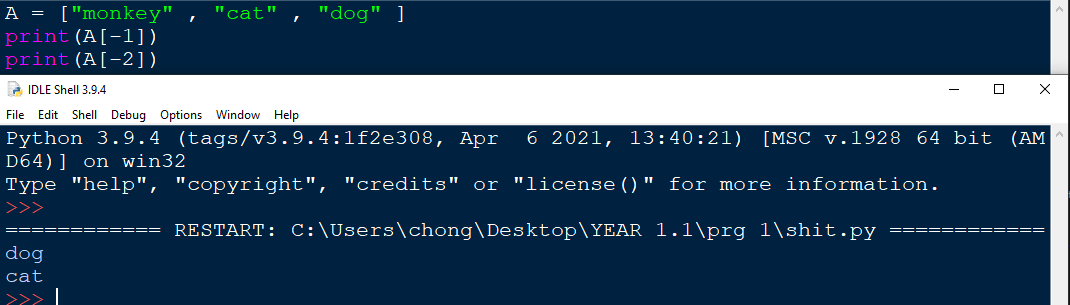
Negative indexes counts the position starting from the back of the list. In this example, the last value and 2nd last value are [-1] and [-2] respectively.
Range of indexes
A range of indexes can be called too, this will allow for multiple selection and editting of data.
the index number is called within the squarebrackets. And infront , the name of the list.
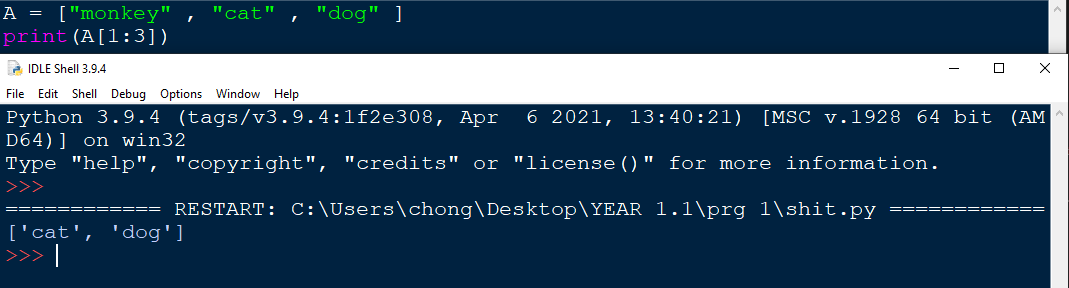
within the square brackets, the range of indexes can be specified. In this case, i would like for the 2nd and 3rd data to be selected and printed, thus [1:3] is called
It should also be noted that the last index is ignored. the range specified is 1 to 3 however the last index will be ignored. Thus only index 1 and 2 are selected.
list length
The length of the list can be determined by using the len() function
.jpg)
List methods
These are some of the other functions that can be used with lists to edit or fetch data.
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
| append() | adds an element at the back of the list. |
| clear() | removes all data from the list. |
| copy() | returns a copy of the list. |
| count() | counts the number of data with a specific value. |
| extend() | adds a list to the back of a pre-existing list. |
| index() | returns specific index of specified data. |
| insert() | inserts data in a specified position. |
| pop() | removes a specific data with reference to position. |
| remove() | removes a specific data with reference to specified value. |
| reverse() | reverses the list's order. |
| sort() | sorts a list. |
End of Python Lists
You have learned Lists in simple terms. Let's proceed on to Quiz.